Data Structure & Implements 1 - Array, Stack, Queue
04 Nov 2018 | c++ 자료 구조
자료 구조
1. Array
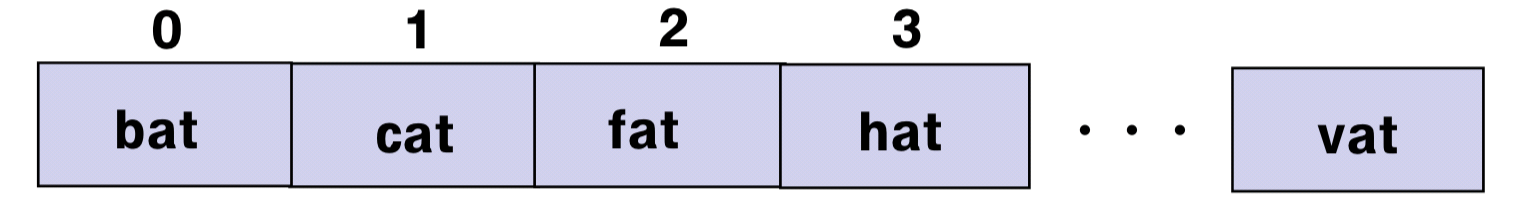
1.1 정의
- A set of pairs, <index, value> such that each index has a value associated with it
- 모든 값은 같은 데이터 타입을 가져야 한다.
- 연속적 메모리 공간에 allocation 됨
- 메모리 사이즈가 정해지면, 런타임 동안에는 수정 불가
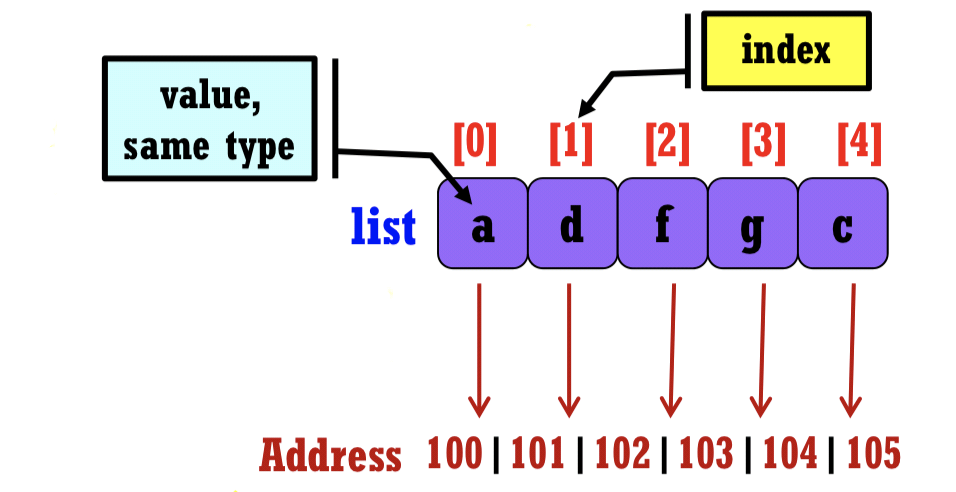
1.2 특징
- Sequential representation
- 메모리 상에 연속적으로 선언되어 있음
- Insert & Delete : Inefficient due to data shift - O(n)
- 데이터를 array 중간에 넣거나 삭제하려면, 나머지 데이터의 이동이 발생하여 비효율 적
- Size of data must be predefined
- 메모리 상에 연속적으로 선언되어야 하므로, array의 크기는 compile time에 미리 선언되어야 함
- Static storage allocation
- 앞과 같은 이유로 프로그램 수행 도중에 사이즈를 바꿀 수 없음
1.3 Operator & Time Complexity
Retrieve(A, i) : array A에 i-index의 값을 가져오기Store(A, i, X) : array A에 i-index에 X값을 넣음
- 위 두개의 operator는 index가 메모리에 위치적으로 연속하기 때문에 direct access가능!, time complexity O(1)
Insert(A, i, X): array A의 i-index에 X값을 삽입
- 위의 Store와 다르게, 뒤쪽에 있는 데이터를 한칸씩 밀어야함
- 비효율적! O(n)
- Delete(A, i) : array A의 i-index의 값을 삭제하고 뒤에 있는 데이터를 당김
- data movement 발생!
- 비효울적! O(n)
1.4 2-Dimensional array
- m & n 의 row, column 테이블이 표현하고 싶을 때 2차원 array 필요
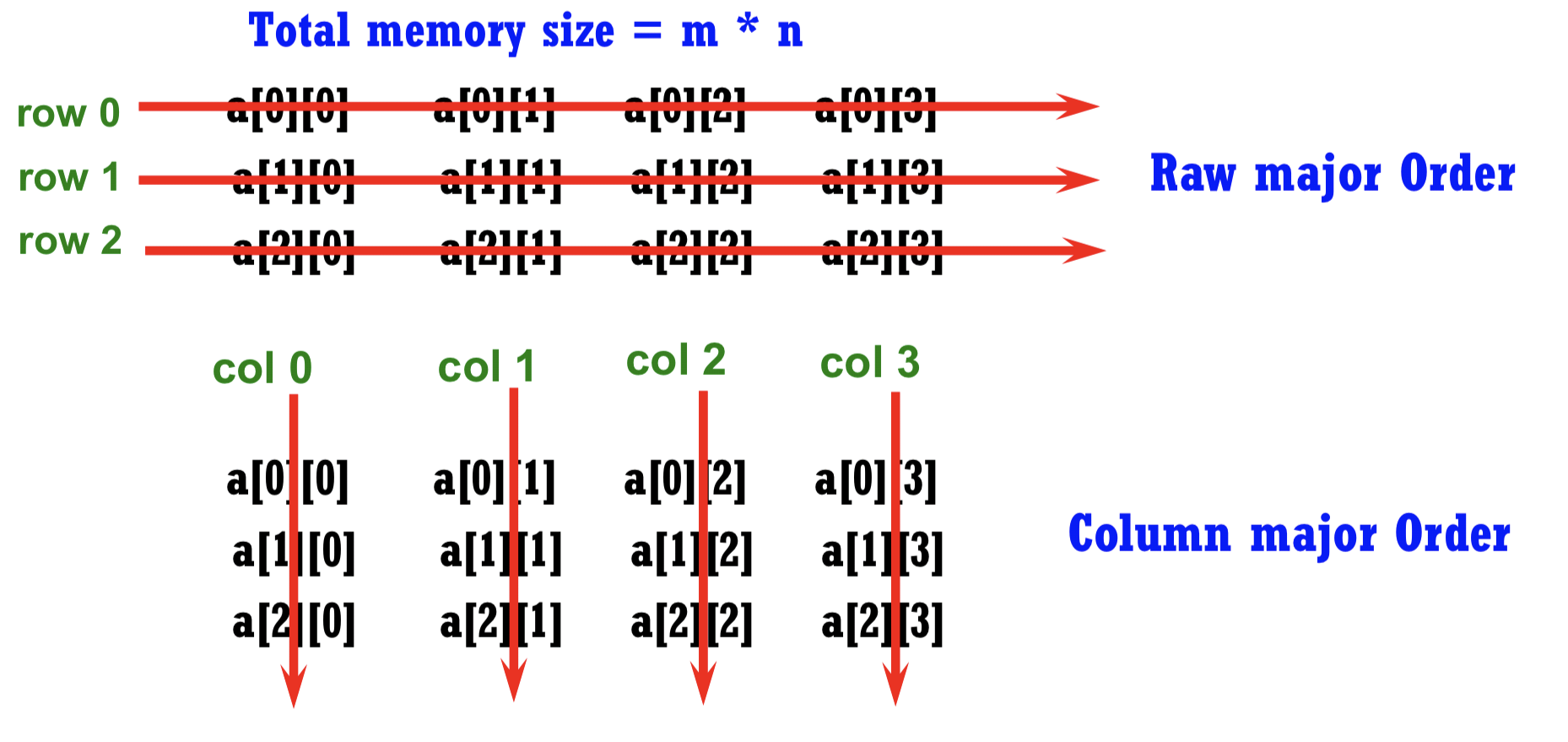
- 대부분의 element가 0인 경우 Sparse Matrix 사용을 고려
- Sparse Matrix : 2-D array ->
<row index, column index, non-zero value>
2. Stack
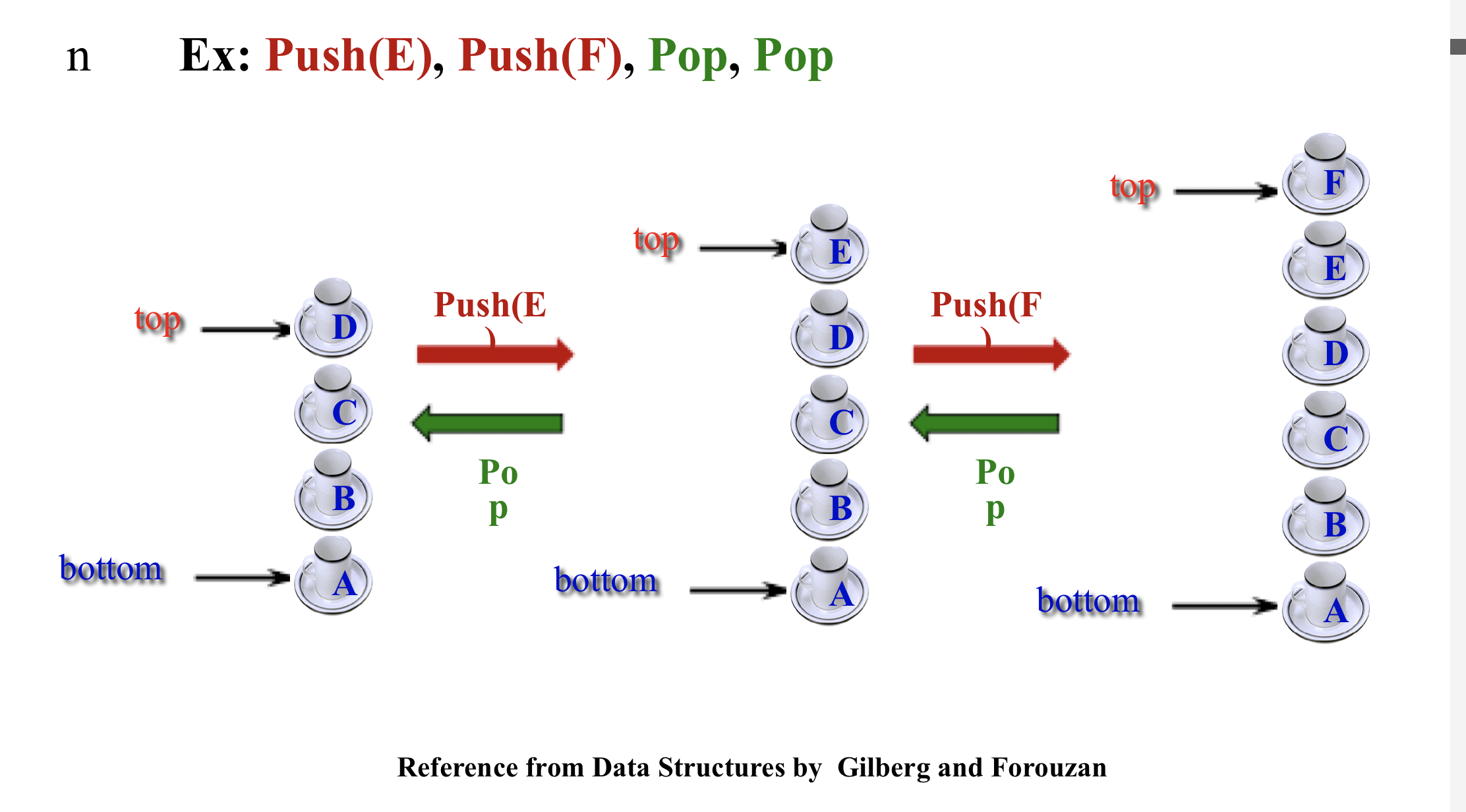
2.1 정의
- A list whose end points are pointed by top and bottom
- 양 마지막 부분이 top과 bottom으로 point된 리스트
- Insertion and deletion take place at the top
- top부분에서만 삽입과 삭제가 이루어진다.
- Bottom is constant, but top grow and shrinks
- Not possibple to access the items within stack, except top!
- LIFO (Last-In First-Out)
2.2 Implementation : Use of array
- Use one-dimensional Array
- Use one variable : top
- Always initialize the top by -1
2.2.1 Operators : Push and pop
- Push : Insert an item into a stack
void push (int top, element item){
if(top >= MAX_STACK_SIZE -1) return stack_full();
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = item;
}
- Pop : Delete an item from a stack
element pop(int top){
if (top == -1) return stack_empty();
item = stack[top];
top = top -1;
}
2.3 Stack의 활용
- Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions
- Maze Problem
- Parsing (Pattern Matching)
- Function Calls/Returns
- Queens Problem
- Backtracking
3. Queue
3.1 정의
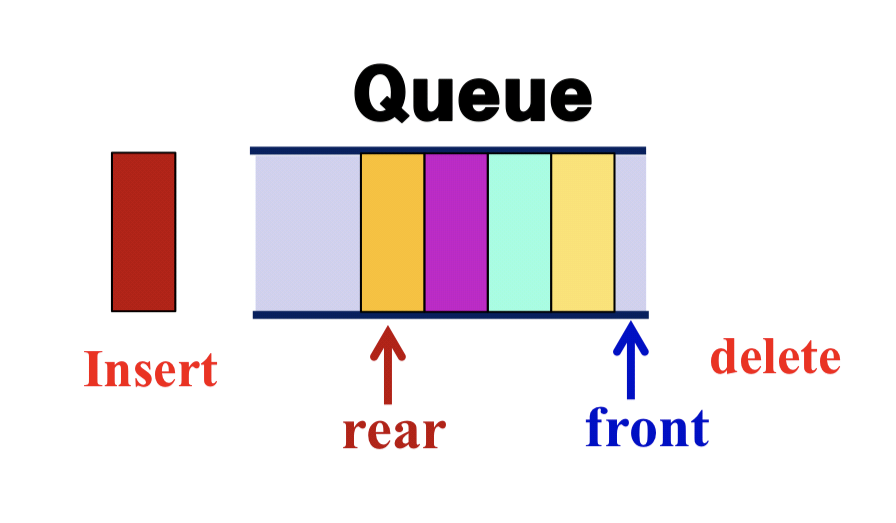
- A list whose ends are pointed by front and rear
- stack과 비슷하면서도 다름
- Insertion and deletion take place at rear and front, repectively
- stack과 다른 점
- Not possible to acceess all items except front and rear
- stack은 top만 접근 가능
- FIFO (First-In First-Out)
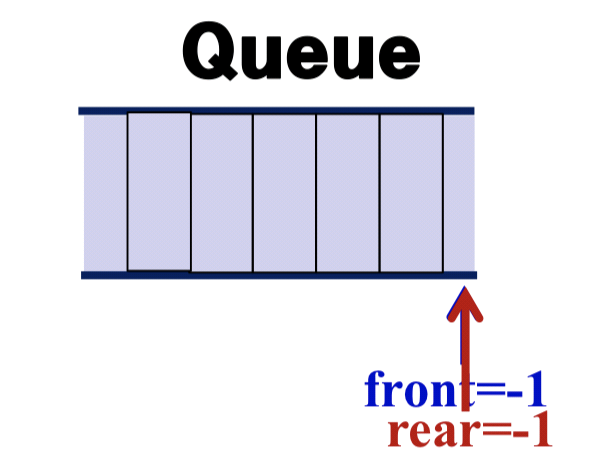
3.2 Implementaion : Use of Array
- Use one-dimensional array
- Use two variables : front, rear
- Initialize always both front and rear by -1
3.2.1 Operators : Insert / Delete
- Insert
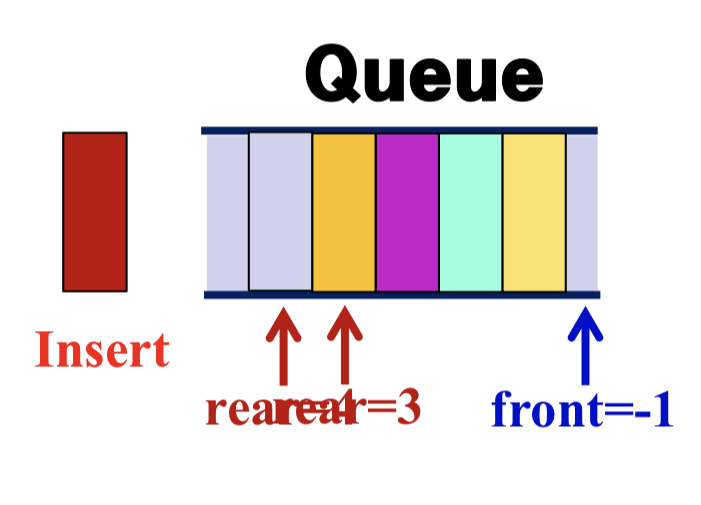
Insert(element item){
if (rear == MAX_Q_SIZE-1) return queue_full();
rear = rear + 1;
queue[rear] = item;
}
- Delete
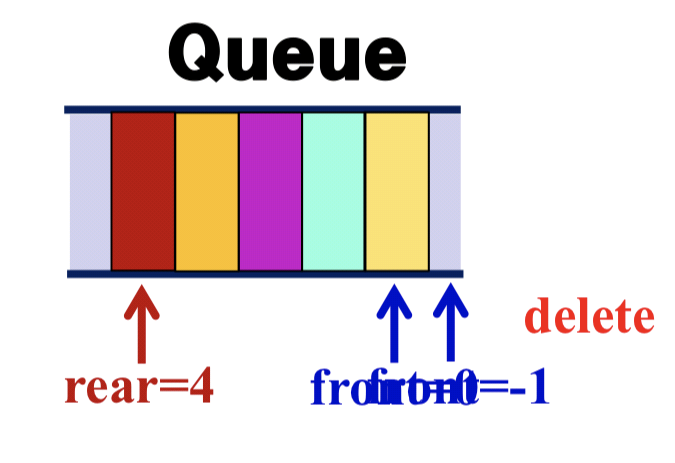
Delete(){
if (front == rear) return queue_empty();
front = front + 1;
item = queue[front];
}
3.3 Problems
- Queue always moves to the right direction.
- Queue_full(i.e.,
rear == MAX_Q_SIZE - 1) condition does not always mean that there are maximum items in queue
- front가 delete() 가 call 될 때마다 +1 되므로, array의 앞부분이 버려진 채로 남게 된다.
- There still may be empty spaces available even if queue is full.
- If you wnat to insert an item, all data should be moved!
- In the worst case, O(n) - Inefficient
- Solution - Circular Queue
3.4 Circular Queue
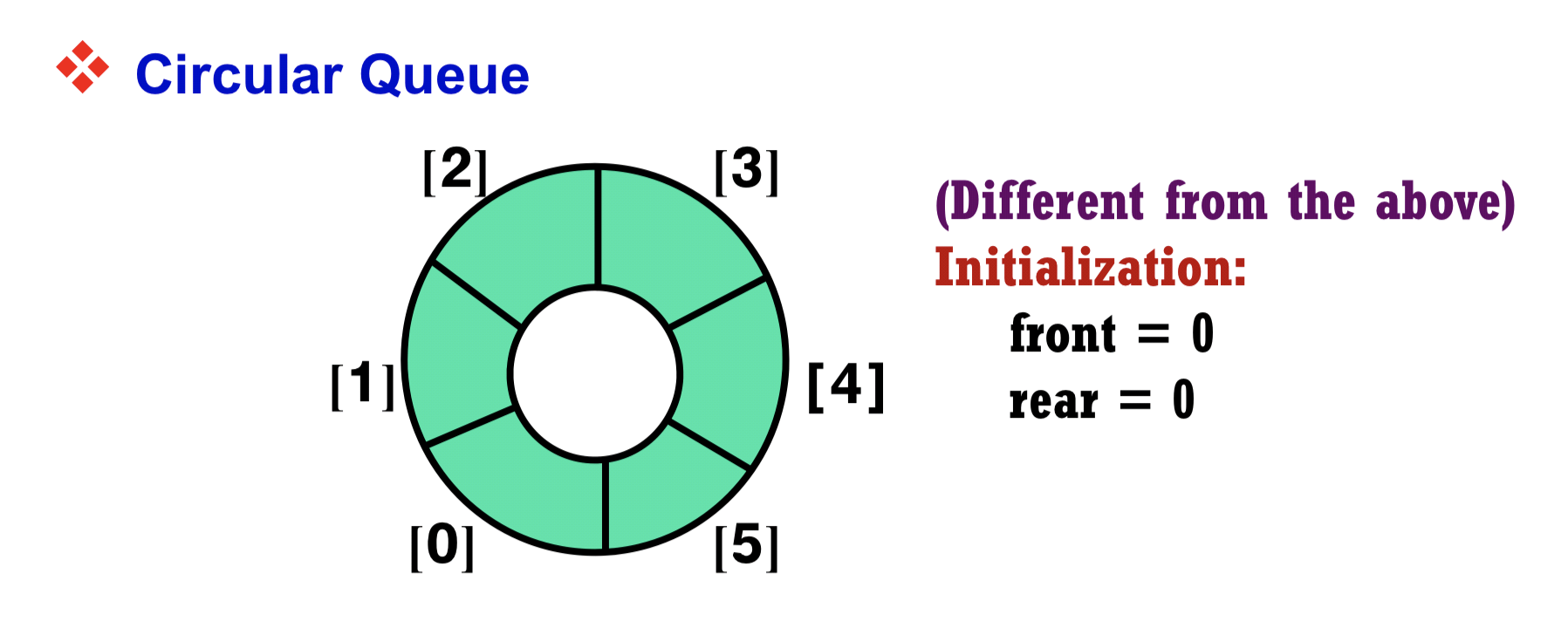
- front + 1 is the same as the actual front value
- rear is the same as the actual rear value
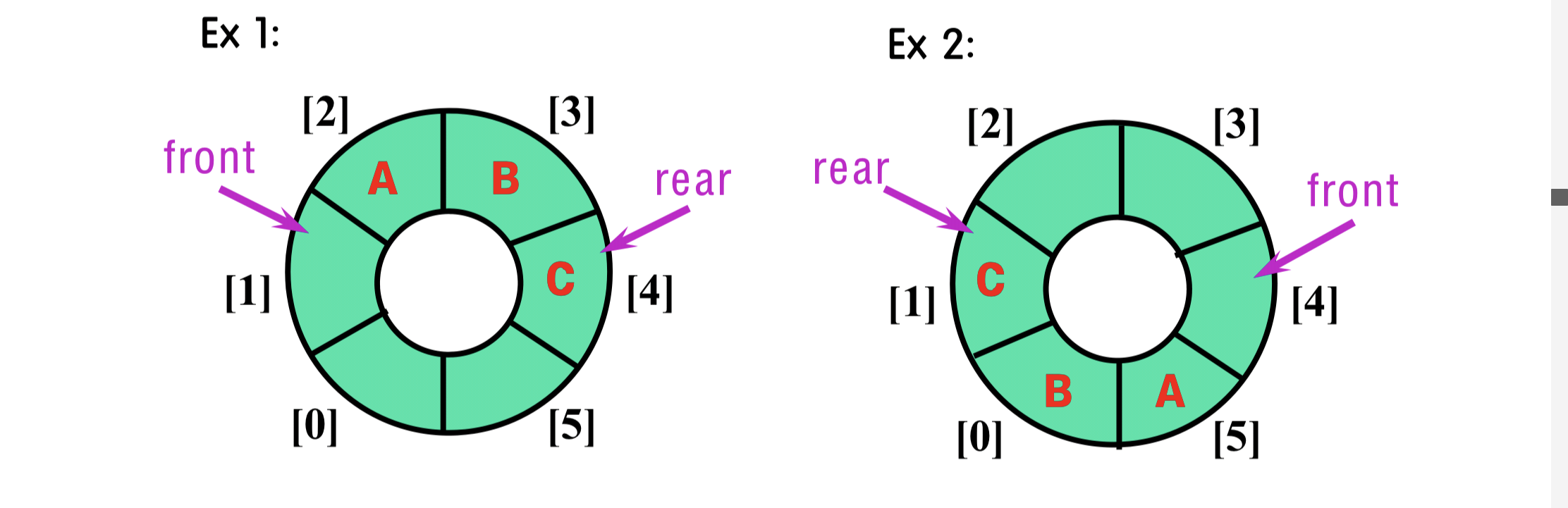
3.4.1 Operator
- Insert
- Increment “rear” by “1” in a clockwise direction;
- if “rear” reaches the end of queue, reset “rear” by “0”
- Queue Full Condition :
front == rear
Insert(element item){
rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_Q_SIZE ///Circluar !
if (front == rear) return queue_full();
queue[rear] = item;
}
- Delete
- Increment “front” by “1” in a clockwise direction;
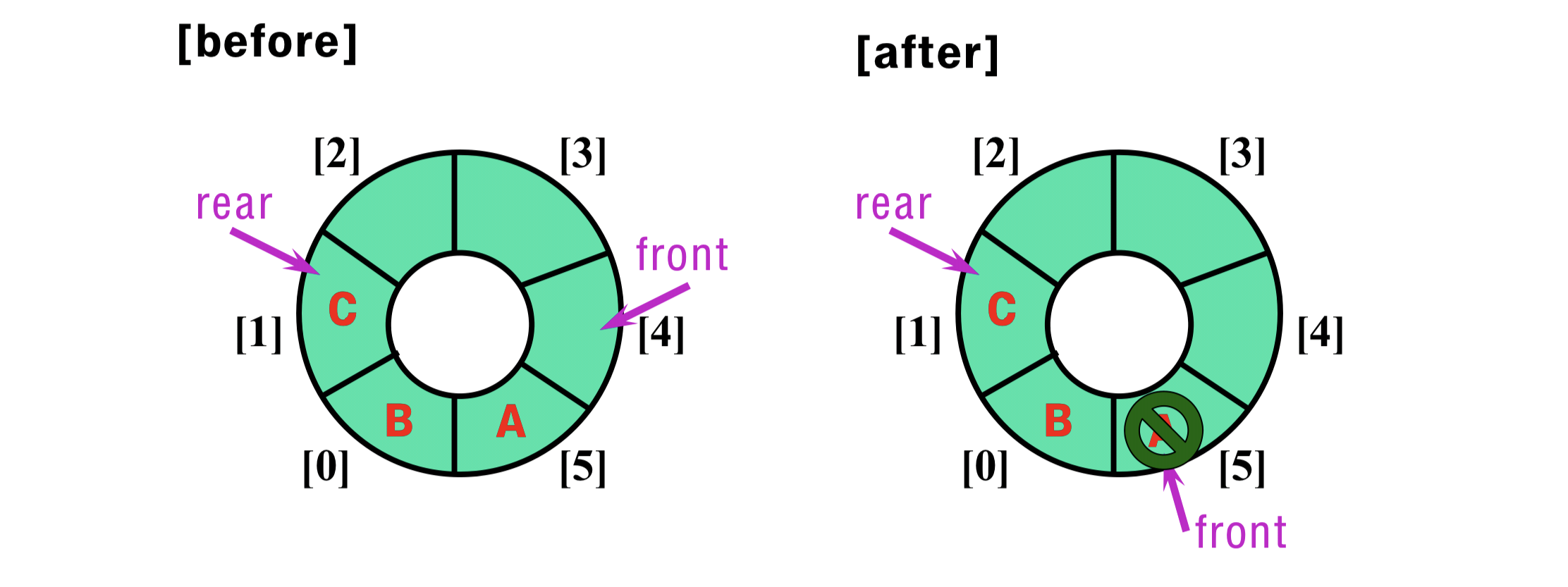
- if “front” reaches the end of queue, reset “front” by “0”
- Condition of Queue Empty : front == rear
Delete(){
if (front == rear) return queue_empty();
front = (front + 1) % MAX_Q_SIZE;
item = queue[front]
}
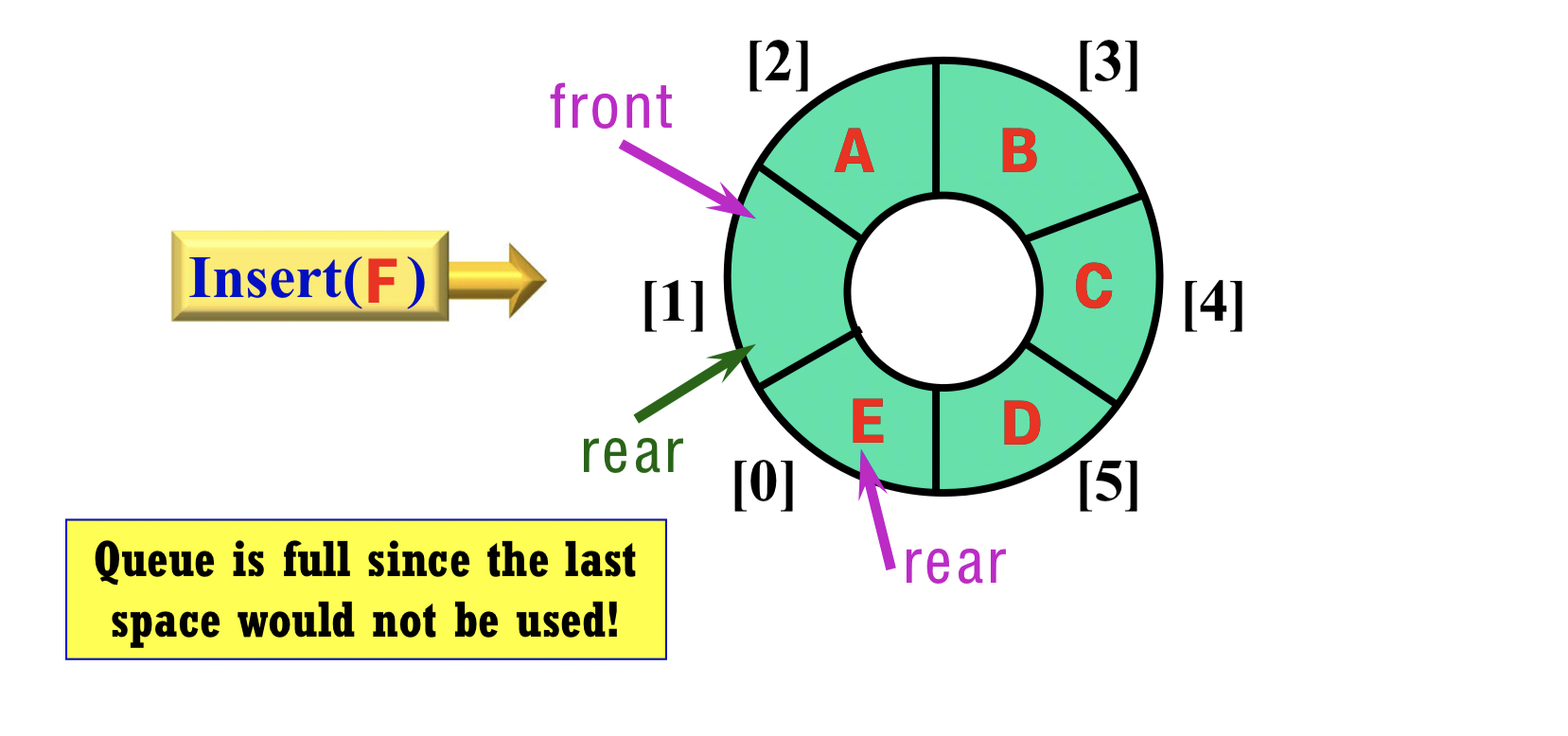
3.5 Problem
- full and empty condition is the same!
- Solution
- option1 :
- Only permit MAX_Q_SIZE -1 elements; (one space in a queue is not used)
- But, at rear == front, reset the rear with the prior position (i.e., rear = rear -1)
- option2 : A Boolean variable (e.g: Tag) is additionally used
- After insert/ delete, set the Tag to true/false
- Queue is empty
if (front == rear) && ! Tag
- Queue is full
if (front == rear) && Tag
3.6 Queue: Applications
- Job Processing (printer, CPU processor)
- Data Buffers
- Waiting times of customers at a public phone
- Deciding number of cashiers (tellers) at super market (bank)
- Traffic Analysis
자료 구조
1. Array

1.1 정의
- A set of pairs, <index, value> such that each index has a value associated with it
- 모든 값은 같은 데이터 타입을 가져야 한다.
- 연속적 메모리 공간에 allocation 됨
- 메모리 사이즈가 정해지면, 런타임 동안에는 수정 불가

1.2 특징
- Sequential representation
- 메모리 상에 연속적으로 선언되어 있음
- Insert & Delete : Inefficient due to data shift - O(n)
- 데이터를 array 중간에 넣거나 삭제하려면, 나머지 데이터의 이동이 발생하여 비효율 적
- Size of data must be predefined
- 메모리 상에 연속적으로 선언되어야 하므로, array의 크기는 compile time에 미리 선언되어야 함
- Static storage allocation
- 앞과 같은 이유로 프로그램 수행 도중에 사이즈를 바꿀 수 없음
1.3 Operator & Time Complexity
Retrieve(A, i): array A에 i-index의 값을 가져오기Store(A, i, X): array A에 i-index에 X값을 넣음- 위 두개의 operator는 index가 메모리에 위치적으로 연속하기 때문에 direct access가능!, time complexity O(1)
Insert(A, i, X): array A의 i-index에 X값을 삽입- 위의 Store와 다르게, 뒤쪽에 있는 데이터를 한칸씩 밀어야함
- 비효율적! O(n)
- Delete(A, i) : array A의 i-index의 값을 삭제하고 뒤에 있는 데이터를 당김
- data movement 발생!
- 비효울적! O(n)
1.4 2-Dimensional array
- m & n 의 row, column 테이블이 표현하고 싶을 때 2차원 array 필요

- 대부분의 element가 0인 경우 Sparse Matrix 사용을 고려
- Sparse Matrix : 2-D array ->
<row index, column index, non-zero value>
- Sparse Matrix : 2-D array ->
2. Stack
2.1 정의
- A list whose end points are pointed by top and bottom
- 양 마지막 부분이 top과 bottom으로 point된 리스트
- Insertion and deletion take place at the top
- top부분에서만 삽입과 삭제가 이루어진다.
- Bottom is constant, but top grow and shrinks
- Not possibple to access the items within stack, except top!
- LIFO (Last-In First-Out)
2.2 Implementation : Use of array
- Use one-dimensional Array
- Use one variable : top
- Always initialize the top by -1
2.2.1 Operators : Push and pop
- Push : Insert an item into a stack
void push (int top, element item){ if(top >= MAX_STACK_SIZE -1) return stack_full(); top = top + 1; stack[top] = item; } - Pop : Delete an item from a stack
element pop(int top){ if (top == -1) return stack_empty(); item = stack[top]; top = top -1; }

2.3 Stack의 활용
- Evaluation of Arithmetic Expressions
- Maze Problem
- Parsing (Pattern Matching)
- Function Calls/Returns
- Queens Problem
- Backtracking
3. Queue
3.1 정의

- A list whose ends are pointed by front and rear
- stack과 비슷하면서도 다름
- Insertion and deletion take place at rear and front, repectively
- stack과 다른 점
- Not possible to acceess all items except front and rear
- stack은 top만 접근 가능
- FIFO (First-In First-Out)
3.2 Implementaion : Use of Array
- Use one-dimensional array
- Use two variables : front, rear
- Initialize always both front and rear by -1

3.2.1 Operators : Insert / Delete
- Insert

Insert(element item){ if (rear == MAX_Q_SIZE-1) return queue_full(); rear = rear + 1; queue[rear] = item; } - Delete

Delete(){ if (front == rear) return queue_empty(); front = front + 1; item = queue[front]; }
3.3 Problems
- Queue always moves to the right direction.
- Queue_full(i.e.,
rear == MAX_Q_SIZE - 1) condition does not always mean that there are maximum items in queue- front가 delete() 가 call 될 때마다 +1 되므로, array의 앞부분이 버려진 채로 남게 된다.
- There still may be empty spaces available even if queue is full.
- If you wnat to insert an item, all data should be moved!
- In the worst case, O(n) - Inefficient
- Solution - Circular Queue
3.4 Circular Queue

- front + 1 is the same as the actual front value
- rear is the same as the actual rear value

3.4.1 Operator
- Insert
- Increment “rear” by “1” in a clockwise direction;
- if “rear” reaches the end of queue, reset “rear” by “0”
- Queue Full Condition :
front == rearInsert(element item){ rear = (rear + 1) % MAX_Q_SIZE ///Circluar ! if (front == rear) return queue_full(); queue[rear] = item; }
- Delete
- Increment “front” by “1” in a clockwise direction;

- if “front” reaches the end of queue, reset “front” by “0”
- Condition of Queue Empty : front == rear
Delete(){ if (front == rear) return queue_empty(); front = (front + 1) % MAX_Q_SIZE; item = queue[front] }
3.5 Problem
- full and empty condition is the same!
- Solution
- option1 :
- Only permit MAX_Q_SIZE -1 elements; (one space in a queue is not used)
- But, at rear == front, reset the rear with the prior position (i.e., rear = rear -1)

- option2 : A Boolean variable (e.g: Tag) is additionally used
- After insert/ delete, set the Tag to true/false
- Queue is empty
if (front == rear) && ! Tag - Queue is full
if (front == rear) && Tag
- option1 :
3.6 Queue: Applications
- Job Processing (printer, CPU processor)
- Data Buffers
- Waiting times of customers at a public phone
- Deciding number of cashiers (tellers) at super market (bank)
- Traffic Analysis
Comments